A Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is an essential component in modern diesel engines, designed to reduce harmful emissions and protect the environment. As stricter regulations on vehicle emissions are enforced, DPF technology plays a critical role in keeping diesel vehicles compliant with these standards. This article will explore what a DPF is, how it works, and why it is crucial for diesel engines.
How Does a Diesel Particulate Filter Work?
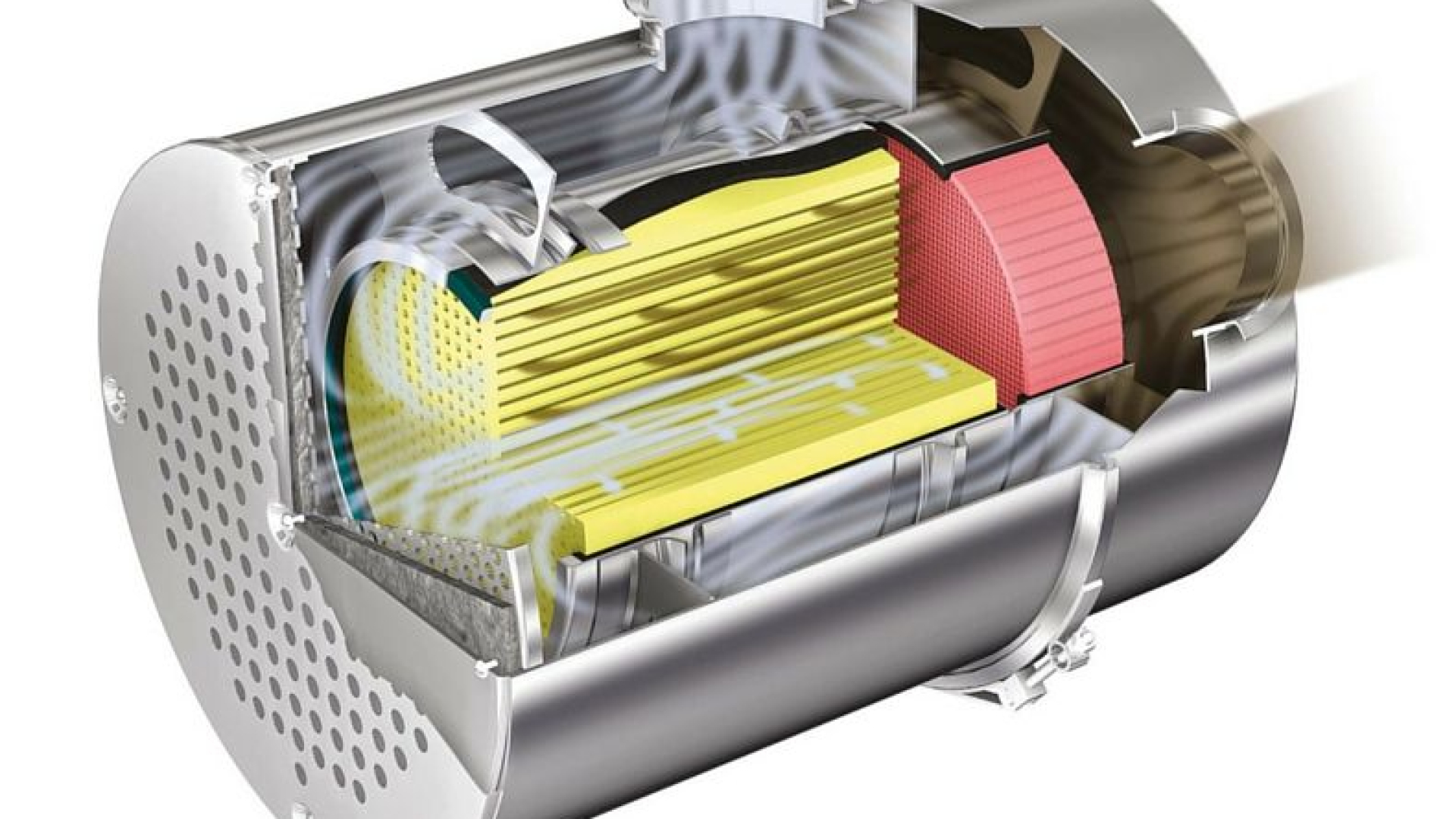
A DPF captures and stores soot particles produced by diesel engines. These particles are harmful to both human health and the environment. The DPF traps the soot and periodically burns it off in a process called regeneration, reducing the overall emissions released into the atmosphere.
There are two primary types of regeneration:
- Passive Regeneration: This occurs automatically when the vehicle is operating at high speeds for extended periods. The high temperature of the exhaust system burns off the accumulated soot.
- Active Regeneration: When passive regeneration is insufficient, the vehicle's system initiates an active regeneration cycle. This involves injecting additional fuel to increase exhaust temperatures and burn off the soot.
Why is a Diesel Particulate Filter Important?
- Environmental Protection: DPFs significantly reduce harmful emissions, such as carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter (PM). This helps to meet stringent emission regulations and reduces the overall impact of diesel vehicles on air quality.
- Compliance with Emission Standards: Countries worldwide are imposing stricter emission standards. Failing to maintain a DPF could result in fines, vehicle failure, or the inability to pass mandatory inspections.
- Improved Vehicle Performance: A well-maintained DPF can enhance the efficiency of the engine by optimizing combustion and reducing exhaust backpressure. Neglecting DPF maintenance, on the other hand, can lead to costly repairs and a decline in engine performance.
Maintenance and Common Issues
DPFs require regular maintenance to prevent clogging and ensure proper regeneration. Clogged DPFs can cause engine malfunctions, decreased fuel efficiency, and costly repairs. Some common symptoms of a clogged DPF include:
- Reduced engine power
- Increased fuel consumption
- Warning lights on the dashboard
Regular cleaning or replacement of the DPF can prevent these issues and prolong the life of the engine.
Conclusion
The Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) is a vital part of modern diesel engines, reducing harmful emissions and ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. Regular maintenance is crucial to keep the filter functioning correctly and to avoid potential engine problems. As emission standards continue to tighten, the importance of DPF technology in diesel vehicles will only increase.
By understanding how the DPF works and ensuring proper upkeep, drivers can protect the environment and extend the life of their diesel engines.




Comments powered by CComment